Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder, and 90% of diabetic disorder belongs to type 2 diabetes. If the fasting blood sugar is above 126 mg/dl/ 7 millimol per litre or the glycated haemoglobin(HbA1c) is more than 48 millimol, one is technically classed as a diabetic patient. The term 'glycated' means attachment of a sugar to a protein or lipid. This gives the average of sugar in the haemoglobin for two months, therefore one need not fast for twelve hours.
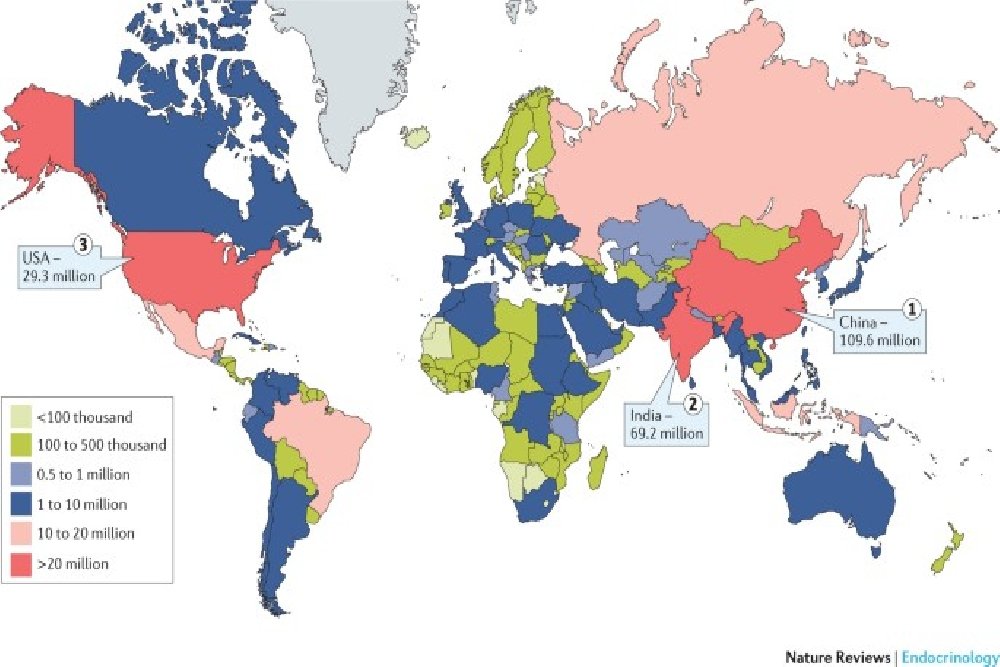
The incidence of Type 2 diabetes is increasing fast because of lifestyle changes which include diet, sedentary work and lack of exercise.Type 2 diabetes is not just due to the lack of insulin produced by the beta cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas, but it is due to the insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. (Insulin resistance means, the effect of insulin on the receptors will be reduced, and there will be antibodies to neutralise the effect of insulin).During the past four decades, the incidence of overweight and obesity has increased, so is the incidence of type 2 diabetes. The prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes is increasing worldwide.

There is a clear genetic predisposition to both type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T2D).The genes of diabetes are associated with that of dementia. Also it is established that diabetes can develop due to mutation of mitochondrial DNA. In the Pacific islands, over 20% people suffer from diabetes, and there is a strong predilection to inheritance.
In this blog, I have described only about the prevalence of diabetes. Genetics is something one cannot control, but what people can control are their lifestyle,diet and weight. The metabolic effect of diabetes is a wide area, which will be addressed in future blogs.
Dr.C.J.George
21st December 2020
Comment Form